Creating Brand Guidelines: Ensuring Consistency in Design and Messaging
In the ever-evolving landscape of business and marketing, maintaining a strong and consistent brand identity is paramount. Brands are more than just logos and taglines; they represent the essence of a company, its values, promises, and unique offerings. In this digital age where consumers are bombarded with countless messages daily, establishing a cohesive brand presence becomes a strategic imperative.
Brand guidelines serve as the blueprint for maintaining consistency in design and messaging across all touchpoints. They encapsulate the visual and verbal elements that define a brand, ensuring that every communication resonates with the desired audience and reinforces the brand’s identity.
This blog will delve into the significance of brand guidelines, exploring how they contribute to brand recognition, consumer trust, and long-term success. By understanding their importance, businesses can unlock the full potential of their brand and create meaningful connections with their target audience.
Defining Your Brand Identity

A robust brand identity lays the foundation for effective communication and resonates with your audience on a deeper level. This section explores the key elements essential for defining your brand identity.
Mission and Values
Your mission statement encapsulates the purpose and core objectives of your brand. It answers the question: Why does your brand exist? It should be concise, memorable, and inspirational, guiding both internal decisions and external messaging.
Values represent the fundamental beliefs and principles that guide your brand’s actions and behaviors. These values should be authentic and aligned with the aspirations of your target audience. They serve as the moral compass for your brand, influencing everything from product development to customer interactions.
Target Audience
Understanding your target audience is crucial for crafting a brand identity that resonates with them. Identify demographic attributes such as age, gender, income level, geographic location, as well as psychographic factors like interests, values, and lifestyle preferences.
Develop detailed buyer personas to humanize your audience segments. These personas should outline the motivations, challenges, and aspirations of your target customers, enabling you to tailor your brand messaging and experiences accordingly.
Conduct market research, surveys, and social listening to gain insights into the needs and preferences of your target audience. By empathizing with their perspective, you can create a brand identity that speaks directly to their desires and aspirations.
Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
Your unique selling proposition distinguishes your brand from competitors and communicates the value proposition to your target audience. It highlights what sets your brand apart and why customers should choose you over alternatives.
Identify the key benefits or advantages that your brand offers to consumers. These could be related to product features, quality, price, convenience, customer service, or emotional appeal.
Craft a compelling and memorable USP that resonates with your target audience and addresses their specific pain points or desires. This statement should be clear, concise, and differentiated, leaving a lasting impression on consumers’ minds.
By defining your brand identity through mission and values, understanding your target audience, and articulating your unique selling proposition, you lay the groundwork for building a strong and differentiated brand. These elements serve as guiding principles that inform your branding decisions and ensure consistency across all touchpoints.
Design Elements for Consistency

Maintaining consistency in design is crucial for reinforcing brand identity and creating memorable brand experiences. This section outlines key design elements that contribute to visual cohesion across all brand touchpoints.
Logo Usage and Variations
Define guidelines for proper usage of the brand logo, including size, placement, and clear space requirements. Ensure that the logo maintains its integrity and legibility across different applications and sizes.
Develop variations of the logo, such as monochrome versions or simplified versions for use in small spaces or digital applications. Clearly outline when each variation should be used to maintain visual consistency.
Color Palette
Establish a cohesive color palette that reflects your brand’s personality and resonates with your target audience. Select primary and secondary colors that evoke the desired emotions and align with your brand values.
Specify color codes (RGB, CMYK, HEX) for digital and print applications to ensure consistency across various mediums. Provide guidelines on color combinations, gradients, and usage proportions to maintain visual harmony.
Typography Guidelines
Choose fonts that complement your brand identity and enhance readability across different platforms. Define primary and secondary typefaces for headlines, body text, and other design elements.
Set guidelines for font sizes, line spacing, and text hierarchy to maintain consistency in typography across all brand communications. Consider accessibility principles to ensure that typography is legible for all users.
Imagery and Photography Style
Establish a cohesive photography style that aligns with your brand’s aesthetic and resonates with your target audience. Define guidelines for image composition, lighting, color treatment, and subject matter.
Curate a library of brand-specific imagery or develop visual themes that convey your brand’s story and values. Ensure that all photographs and illustrations reflect the diversity and inclusivity of your audience.
Iconography and Graphics
Create a set of custom icons and graphics that complement your brand’s visual language and enhance communication. Define a consistent style for icons, illustrations, and other graphic elements.
Provide guidelines on iconography usage, including size, color, and alignment. Ensure that icons maintain clarity and scalability across different resolutions and devices.
By establishing clear guidelines for logo usage and variations, color palette, typography, imagery and photography style, as well as iconography and graphics, you can ensure visual consistency across all brand communications. These design elements work together to reinforce your brand identity and create cohesive brand experiences for your audience.
Messaging Guidelines

Crafting a consistent and compelling brand message is essential for building trust, resonating with your audience, and driving engagement. This section outlines key messaging guidelines that help maintain coherence and effectiveness in communication.
Tone of Voice
Define the tone of voice that aligns with your brand’s personality and resonates with your target audience. Consider attributes such as friendly, professional, conversational, authoritative, or playful.
Provide examples and descriptive language to illustrate the desired tone of voice in various contexts. Ensure consistency in tone across all communication channels and touchpoints.
Brand Voice Attributes
Identify the key attributes that define your brand’s voice and distinguish it from competitors. These attributes may include qualities such as authentic, innovative, empathetic, or inspirational.
Develop guidelines for incorporating brand voice attributes into messaging, ensuring that every communication reflects the essence of your brand and reinforces its unique identity.
Messaging Hierarchy
Establish a messaging hierarchy that prioritizes key themes and brand narratives. Define overarching brand messages, as well as supporting messages that convey specific benefits or features.
Organize messaging hierarchy based on audience needs and communication goals. Ensure that each level of messaging aligns with the overall brand positioning and resonates with target audience segments.
Key Messaging Points
Identify the core messages that you want to communicate consistently across all brand touchpoints. These key messaging points should encapsulate your brand’s value proposition, unique selling points, and customer benefits.
Develop clear and concise messaging statements that address customer pain points, highlight competitive advantages, and reinforce brand positioning. Tailor messaging to resonate with different audience segments and communication channels.
By establishing clear guidelines for tone of voice, brand voice attributes, messaging hierarchy, and key messaging points, you can ensure consistency and effectiveness in your brand communication efforts. These messaging guidelines serve as a roadmap for crafting compelling and resonant messages that connect with your audience and drive desired outcomes.
Typography Guidelines
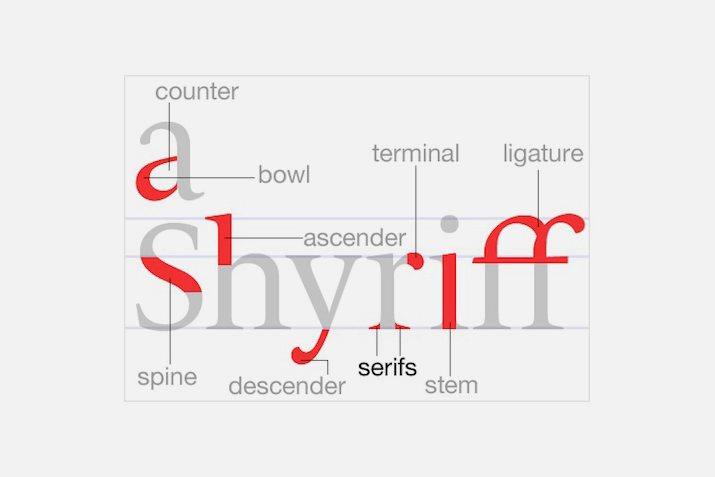
Typography plays a significant role in shaping the visual identity of a brand and ensuring readability across various platforms. This section outlines key considerations and guidelines for effective typography usage in brand communication.
Font Selection
Choose fonts that align with your brand identity, values, and target audience preferences. Select primary and secondary typefaces that reflect the desired tone and personality of your brand.
Consider factors such as readability, legibility, and scalability across different devices and mediums. Avoid overly decorative or trendy fonts that may compromise readability or brand consistency over time.
Font Pairing
Establish a harmonious pairing of fonts for headlines, body text, and other design elements. Ensure that primary and secondary typefaces complement each other while providing visual contrast and hierarchy.
Test font combinations to ensure readability and visual coherence across various communication materials. Strive for a balanced and cohesive typographic palette that enhances brand messaging and aesthetics.
Font Sizes and Hierarchy
Set guidelines for font sizes to maintain consistency and hierarchy in typography across all brand communications. Define appropriate font sizes for headlines, subheadings, body text, and other textual elements.
Establish a clear hierarchy of text elements to guide readers’ attention and convey information effectively. Use variations in font size, weight, and style to differentiate between different levels of information and importance.
Line Spacing and Alignment
Define guidelines for line spacing (leading) to optimize readability and legibility of text blocks. Ensure adequate spacing between lines to prevent overcrowding and improve text flow.
Align text consistently to maintain visual order and coherence in typography. Choose alignment options such as left-aligned, justified, or centered based on readability and design aesthetics.
Accessibility Considerations
Consider accessibility principles when selecting fonts and defining typography guidelines. Choose fonts that are legible and accessible for users with visual impairments or reading disabilities.
Ensure sufficient color contrast between text and background to enhance readability for users with low vision or color vision deficiencies. Test typography choices using accessibility tools and guidelines to ensure inclusivity and compliance.
By following typography guidelines that address font selection, pairing, sizes, hierarchy, and accessibility considerations, you can create a cohesive and visually engaging brand identity across all communication channels. Consistent typography enhances readability, reinforces brand messaging, and contributes to a positive user experience for your audience.
Collaborative Processes and Approval Procedures

Effective collaboration and streamlined approval processes are essential for ensuring the successful implementation of brand guidelines. This section outlines key steps and best practices for involving stakeholders, establishing review and feedback loops, and finalizing approvals.
Involving Stakeholders
Identify key stakeholders who play a role in brand development, implementation, and management. This may include executives, marketing teams, design teams, sales representatives, and external partners.
Establish clear roles and responsibilities for each stakeholder involved in the brand development process. Ensure that stakeholders understand the importance of adhering to brand guidelines and actively participate in the decision-making process.
Review and Feedback Loops
Implement a structured review and feedback process to gather input from relevant stakeholders at key stages of brand development. This may include design concept reviews, content reviews, and usability testing.
Set clear deadlines and milestones for feedback collection to keep the project on track and ensure timely revisions. Encourage constructive feedback and open communication to address any concerns or suggestions effectively.
Final Approval Process
Define a formalized final approval process to sign off on brand guidelines and related assets. Establish clear criteria and checkpoints for evaluating compliance with brand standards, consistency across various elements, and alignment with strategic objectives.
Designate individuals or committees responsible for final approval, ensuring representation from relevant departments and ensuring that decisions are aligned with overall business goals.
Document approval decisions and any revisions made during the review process for future reference and accountability. Communicate approved brand guidelines and assets to all stakeholders to ensure consistent implementation across all channels.
By involving stakeholders, establishing review and feedback loops, and implementing a structured final approval process, you can ensure that brand guidelines are developed collaboratively, refined effectively, and ultimately approved with confidence. These collaborative processes foster engagement, accountability, and alignment across the organization, leading to the successful implementation and maintenance of consistent brand identity and messaging.
Documenting and Distributing Brand Guidelines
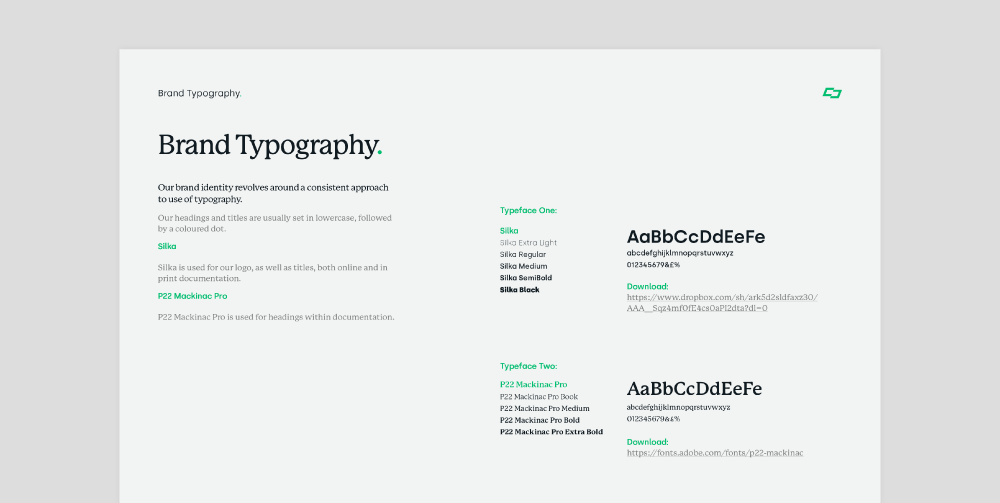
Once brand guidelines are established, it’s crucial to document them effectively and ensure widespread access and understanding across the organization. This section covers key strategies for creating a comprehensive guide, making guidelines accessible, and implementing training and onboarding processes.
Creating a Comprehensive Guide
Compile all brand guidelines, including design elements, messaging principles, and usage rules, into a comprehensive document or brand manual. Organize information logically, using clear headings, sections, and visual examples to enhance readability and comprehension.
Include detailed explanations, rationale, and best practices for each guideline to provide context and guidance for users. Use visuals, such as diagrams, illustrations, and examples, to reinforce key concepts and demonstrate proper implementation.
Regularly update the brand guidelines document to reflect any changes or revisions, ensuring that it remains accurate and relevant over time. Version control and document management systems can help track updates and ensure that all users have access to the latest version.
Making Guidelines Accessible
Distribute the brand guidelines document through accessible channels to ensure that all relevant stakeholders can easily access and reference it. Consider digital formats such as PDFs, online portals, or intranet sites, as well as printed copies for offline use.
Provide clear instructions on how to access and navigate the brand guidelines document, including table of contents, search functionality, and bookmarks for easy reference. Ensure compatibility with different devices and screen sizes to accommodate diverse user preferences.
Promote awareness and visibility of the brand guidelines within the organization through email announcements, training sessions, and internal communications. Encourage employees to familiarize themselves with the guidelines and use them as a reference in their daily work.
Training and Onboarding Processes
Implement training programs and onboarding processes to educate employees and stakeholders on the importance of brand consistency and the use of brand guidelines. Offer workshops, webinars, or online courses to provide hands-on guidance and practical examples.
Incorporate brand guidelines into employee orientation materials and onboarding documentation to ensure that new hires are introduced to brand standards from the outset. Include quizzes or assessments to gauge understanding and reinforce learning objectives.
Provide ongoing support and resources, such as brand ambassadors or help desks, to address questions, clarify guidelines, and provide guidance on specific use cases or scenarios. Encourage a culture of ownership and accountability for upholding brand standards across the organization.
By documenting brand guidelines comprehensively, making them accessible to all stakeholders, and implementing training and onboarding processes, you can empower employees to uphold brand consistency and integrity in their daily activities. Effective distribution and education ensure that brand guidelines are not only understood but also embraced as essential tools for achieving organizational goals and delivering cohesive brand experiences.
Monitoring and Updating Guidelines

Brand guidelines are not static documents; they require regular monitoring, feedback, and updates to remain relevant and effective. This section outlines key strategies for monitoring compliance, gathering feedback, and evolving guidelines to reflect brand growth and changes.
Regular Audits for Compliance
Conduct periodic audits to assess adherence to brand guidelines across various touchpoints and channels. Evaluate visual consistency, messaging alignment, and overall brand representation to identify any deviations or inconsistencies.
Utilize audit tools and checklists to streamline the process and ensure comprehensive coverage of all brand elements and assets. Assign responsibility for conducting audits to designated individuals or teams within the organization.
Feedback Mechanisms
Establish feedback mechanisms to solicit input from stakeholders, including employees, customers, and external partners, on the effectiveness and relevance of brand guidelines. Encourage open communication and constructive criticism to gather valuable insights for improvement.
Implement surveys, focus groups, or feedback forms to gather qualitative and quantitative feedback on brand perception, usability of guidelines, and areas for enhancement. Analyze feedback trends and prioritize actionable recommendations for updating guidelines.
Feedback Mechanisms
Monitor market trends, industry developments, and changes in consumer behavior to identify opportunities and challenges that may impact the brand’s positioning or messaging. Stay agile and responsive to evolving market dynamics to maintain relevance and competitive advantage.
Regularly review and update brand guidelines to incorporate new insights, best practices, and innovations that align with the brand’s strategic objectives and growth trajectory. Considerations may include emerging design trends, evolving customer preferences, and technological advancements.
Engage key stakeholders, including senior leadership, marketing teams, and creative agencies, in the process of updating brand guidelines to ensure alignment with overarching business goals and brand vision. Collaborate cross-functionally to integrate diverse perspectives and expertise into guideline revisions.
By implementing regular audits for compliance, establishing feedback mechanisms, and evolving guidelines in line with brand growth, organizations can ensure that brand guidelines remain effective tools for maintaining consistency, relevance, and resonance with target audiences. Embracing a proactive approach to monitoring and updating guidelines enables brands to adapt to changing market dynamics and seize opportunities for sustained success and growth.
Conclusion: The Power of Consistent Branding
Consistency in branding is not just a concept; it’s a strategic imperative that can elevate a brand from ordinary to extraordinary. Throughout this exploration of brand guidelines and their importance, we’ve uncovered the myriad ways in which consistent branding can impact businesses positively.
First and foremost, consistent branding builds trust. When customers encounter a brand with a consistent visual identity, tone of voice, and messaging across various touchpoints, it instills confidence and reliability. This trust forms the foundation of strong customer relationships, leading to increased loyalty and advocacy.
Consistent branding also enhances brand recognition. Through repetition and reinforcement of key brand elements, such as logos, colors, and typography, brands become more memorable and recognizable. This increased visibility helps cut through the noise in crowded markets and ensures that the brand stands out in consumers’ minds.
Furthermore, consistent branding fosters brand coherence and alignment. When every aspect of a brand’s communication reflects its core values, mission, and personality, it creates a unified brand experience. This cohesion resonates with customers on a deeper level, forging emotional connections and differentiation from competitors.
Moreover, consistent branding streamlines marketing efforts and drives efficiencies. By having established guidelines for design, messaging, and communication, businesses can produce content more efficiently, reduce errors, and optimize resources. This enables brands to focus on delivering impactful experiences and driving business results.
Finally, consistent branding enables brand evolution and growth. While the essence of a brand remains consistent, brand guidelines also allow for adaptation and innovation as the business evolves. By regularly auditing and updating brand guidelines, businesses can ensure that their brand remains relevant, responsive to market changes, and reflective of evolving consumer preferences.


